The Identity Breach That Cost Us Our Reputation
How a single security oversight exposed sensitive candidate data, leading to a massive reputational hit.
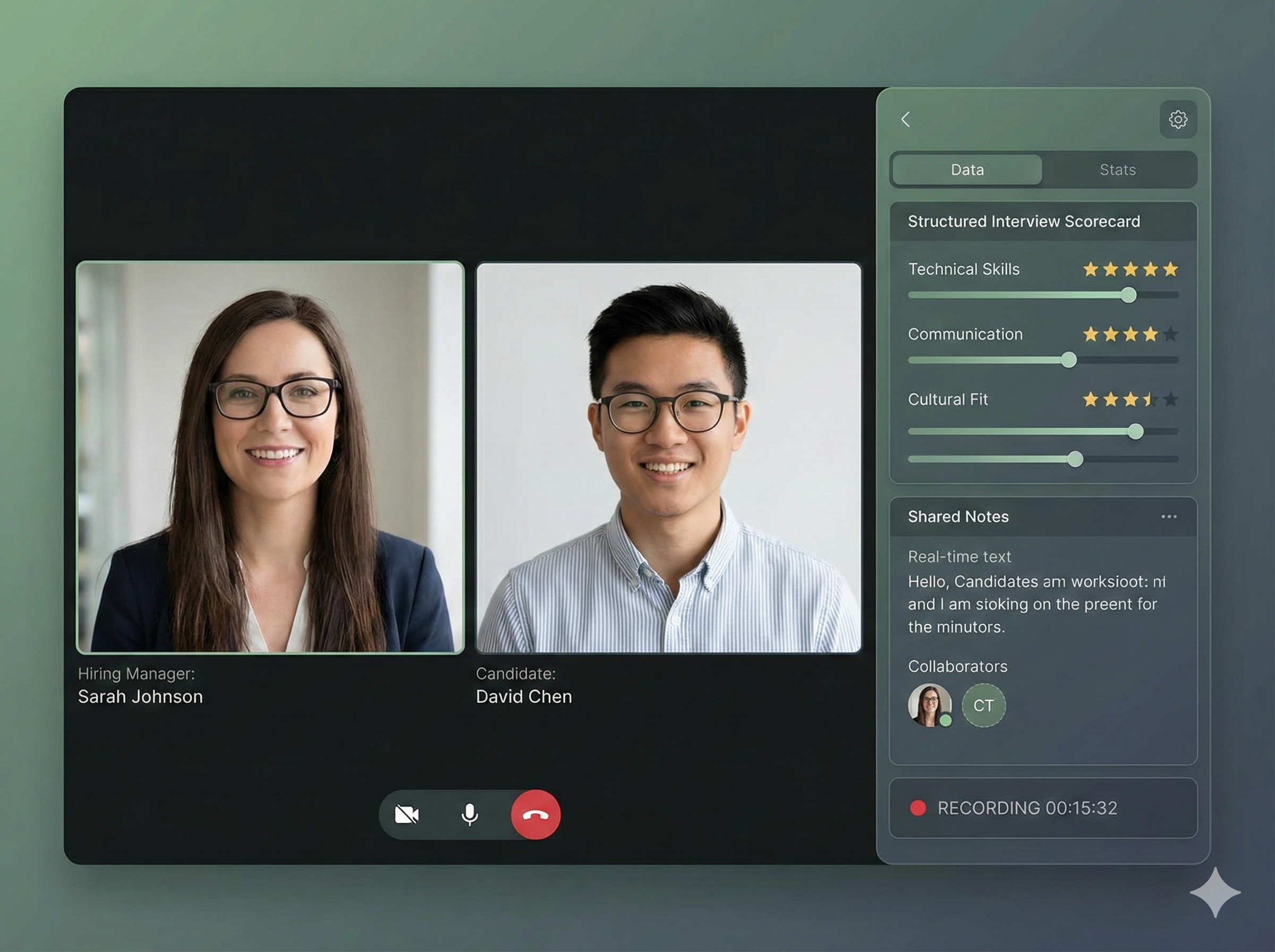
A single security oversight can cost you your reputation and millions in fines.Back to all posts
The Identity Breach That Cost Us Our Reputation
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, a single security oversight can lead to catastrophic consequences. Imagine this: your team just deployed a new candidate verification system, but due to a misconfigured access control, a malicious actor gains access to sensitive candidate data. The fallout? A breach that not only exposes personal information but also leads to a loss of trust and a potential $250,000 in regulatory fines. This scenario is all too common and serves as a stark reminder of the necessity for robust security measures.
Why This Matters
Implementing a least-privilege access model is not merely a best practice; it is essential. By restricting access to only those who absolutely need it, you minimize your attack surface. This strategy should be complemented by regular secret rotation, ensuring that even if credentials are compromised, their usability is limited. Additionally, encrypted evidence handling—specifically using AES-256 encryption both in transit and at rest—provides an added layer of security, safeguarding sensitive data from unauthorized access.
How to Implement It
To implement these strategies effectively, consider the following steps: 1. Establish Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Define roles within your organization and assign permissions based on the principle of least privilege. This ensures that employees can only access the data necessary for their job functions. Utilize tools like AWS IAM or Azure RBAC to streamline this process. 2. Automate Secret Rotation: Use tools like HashiCorp Vault or AWS Secrets Manager to automate the rotation of secrets. Set a regular cadence for rotation based on your risk assessment. This reduces the window of opportunity for potential attackers. 3. Enforce AES-256 Encryption: Ensure that all sensitive data is encrypted both in transit and at rest. This can be implemented using TLS for data in transit and AES-256 for stored data on your databases and file systems. Regularly audit your encryption practices to ensure compliance with industry standards.

Key Takeaways
Key insights from these strategies include: - Always validate access requests: Ensure that access is granted based on current roles and responsibilities. - Monitor and log access attempts: Use tools like Splunk or ELK Stack for real-time monitoring and auditing of access logs. - Educate your team: Regular security training can help prevent social engineering attacks that target user credentials.
Key takeaways
- Implement least-privilege access to minimize risk exposure.
- Regularly rotate secrets to prevent unauthorized access.
- Utilize AES-256 encryption for data in transit and at rest.
Implementation checklist
- Establish role-based access control (RBAC) for all systems.
- Set up automated secret rotation processes using tools like HashiCorp Vault.
- Ensure AES-256 encryption is enforced for all sensitive data.
Questions we hear from teams
- What is least-privilege access and why is it important?
- Least-privilege access restricts user permissions to only those necessary for their role, minimizing the risk of data exposure.
- How often should secrets be rotated?
- Secrets should be rotated based on your risk assessment, typically every 30 to 90 days, depending on sensitivity.
- What is AES-256 encryption?
- AES-256 is a strong encryption standard that secures data both in transit and at rest, providing robust protection against unauthorized access.
Ready to secure your hiring pipeline?
Let IntegrityLens help you verify identity, stop proxy interviews, and standardize screening from first touch to final offer.
Watch IntegrityLens in action
See how IntegrityLens verifies identity, detects proxy interviewing, and standardizes screening with AI interviews and coding assessments.
